FAQ
chrisreidy@arizona.edu
sarawillis@arizona.edu
ric@arizona.edu
Account Access
- You haven't created an account yet.
- Your account isn't sponsored yet.
- You aren't using two-factor authentication (NetID+).
- You need to wait 15 minutes. If you just created your account, it takes time before you can log in.
- You're trying to connect using ssh NetID@login.hpc.arizona.edu. This will not work. Instead, use: ssh NetID@hpc.arizona.edu.
- You're using NetID@hpc.arizona.edu or NetID@email.arizona.edu as your username in PuTTY. Instead, use only your NetID.
- You've entered your password incorrectly too many times. After multiple failed password entries, the system will place a 60 minute ban on your account for security reasons.
This error appears when you have entered your password incorrectly too many times. A security lock is automatically put in place for 60 minutes. After multiple failed password entries, the system will place a 60 minute ban on your account for security reasons. If you wait until 60 minutes has elapsed, you can try to log in again.
This specific error shows up when your NetID has been locked, usually due to multiple failed login attempts when trying to access university services. Contact 24/7 to unlock your account: https://it.arizona.edu/get-support
- Ensure you are using the correct password. Sometimes typing your password into a plain text file and copying/pasting it into the terminal can help.
- You need to wait about 15 minutes after your account is approved for the account to be available
- You must enroll in NetId. Depending on the application you use to log in, you may not get the typical NetID+/DUO menu of options, or an error message indicating this is your problem
HPC uses the same NetID login credentials as all UA services. If you need to reset your NetID password you can do so using the NetID portal: https://netid-portal.iam.arizona.edu/
Faculty members who manage their own HPC groups can follow the instructions in our Research and Class Groups page.
Yes, if you are a former university affiliate or campus collaborator participating in research, you may register as a Designated Campus Colleague (DCC). Once your DCC status has been approved, you will receive a NetID+ which you may use to create an HPC Account. If you already have an HPC Account, no further action is required.
General Computing
When you log into HPC, the variable $COMMAND_PROMPT is set to your current cluster (e.g.: (puma)). Sometimes this can cause formatting problems. If you'd prefer to modify your $PS1, you can add the following to your ~/.bashrc:
if [ -n "${PROMPT_COMMAND}" -a -r /usr/local/bin/slurm-selector.sh ]; then
SavePS1=${PS1}
Cur_Cluster=$(eval ${PROMPT_COMMAND} 2>/dev/null)
PS1="${Cur_Cluster}${SavePS1}"
unset PROMPT_COMMAND
for c in puma ocelote elgato; do
alias ${c}="PS1=\"(${c}) ${SavePS1}\"; . /usr/local/bin/slurm-selector.sh ${c}; unset PROMPT_COMMAND"
done
unset Cur_Cluster SavePS1
fi
These files are called core dumps and may be created when a program terminates abnormally. Core dumps contain the system's memory at the time of the fault event as well as additional information that can be used with a debugger (e.g. gdb) to track down the source of the error.
One drawback to core dump files is they can be quite large. If you're working with limited space (e.g., your home directory or a nearly-full /groups or /xdisk) or are running many jobs, you may consider disabling them. To do this, include the following line in your batch script before your program's execution:
ulimit -c 0
Open OnDemand
This is most commonly seen with users who have Anaconda or Miniconda initialized in their accounts. For a permanent solution, you can run the following command from an interactive terminal session:
conda config --set auto_activate_base false
This will prevent conda from auto-activating when you first log in and allow you to have more control over your environment. When you'd like to activate anaconda, run conda activate. See this example for information running anaconda workflows in batch with auto-activation disabled.
If you are trying to log in to Open Ondemand and are seeing the following:
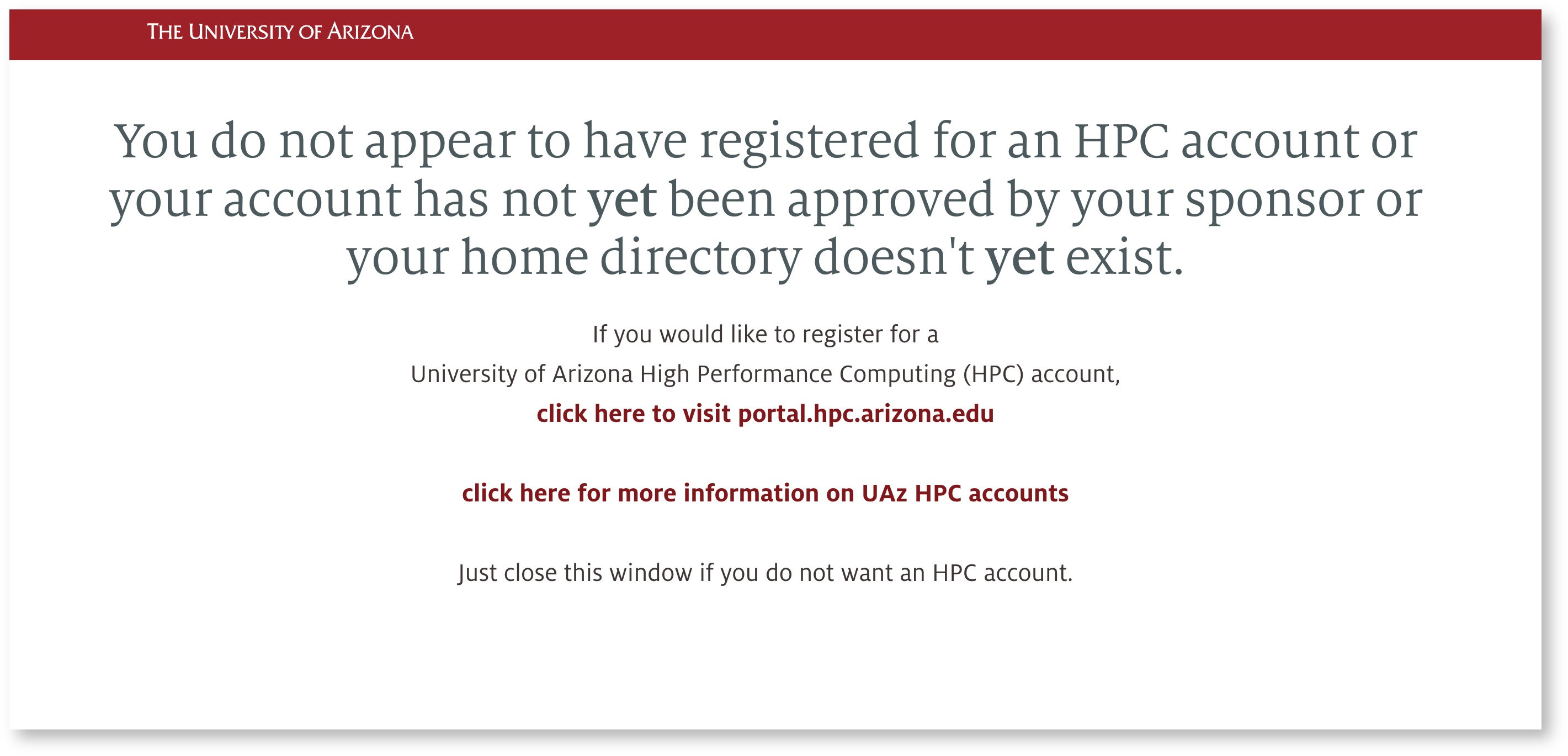
- You have not yet been sponsored by a faculty member. See our Account Creation page for instructions on getting registered for HPC.
- If you are already registered for HPC, this may be a browser issue. Try logging in again in an incognito session or different browser to test. If this succeeds, clearing your browser's cookies should help.
If you are trying to log in to Open Ondemand and are seeing the following:
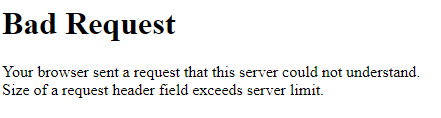
this may be a browser issue. Try logging in again in an incognito session or different browser to test. If this succeeds, clearing your browser's cache should help.
If you're trying to log into Open OnDemand but are getting an ambiguous error that looks something like the following:
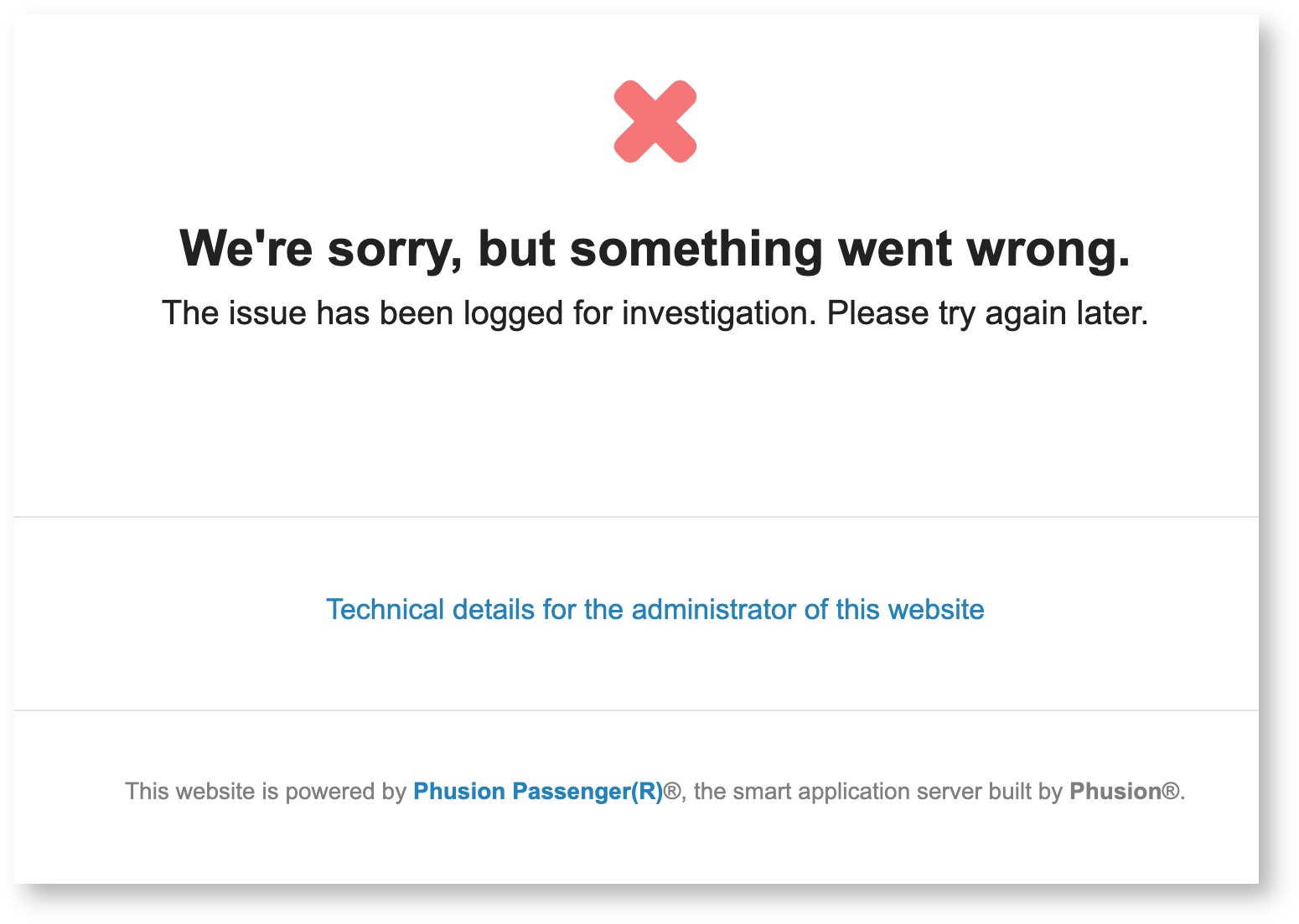
check your storage usage in your home directory. You can do this by logging into HPC in a terminal session and using the command uquota. If your storage usage is >50GB, OnDemand cannot create the temporary files necessary to give access to the website. Try clearing out some space in your home and then logging back into OnDemand.
Jobs and Scheduling
There are a few reasons your job may not be running, check below for some ideas on diagnosing the issue:
- Run
squeue --job <jobid>and see if there is anything listed under "(REASON)". This may give an idea why your job is stuck in queue. We have a table in our SLURM documentation that describes what each Reason code means. - Due to the number of HPC users, it may not always be possible to run a submitted job immediately. If there are insufficient resources available, your job will be queued and it may take up to a few hours for it to begin executing.
- Your group may have run out of standard hours. You can check your allocation using the command
va. - Your group/job has reached a resource usage limit (e.g., number of GPUs that may be used concurrently by a group, or a job has requested more than the 10 day max walltime). Try running
job-limits <group_name>to see what limits you're subject to and if there are any problem jobs listed. - You may be requesting a rare resource (e.g., 4 GPUs on a single node on Puma or a high memory node).
- If you are requesting a single GPU on Puma and are frustrated with the wait times, you might consider checking if Ocelote will work for your analyses. There are more GPU nodes available on that cluster with shorter wait times.
- If you are trying to run a job on a standard node and have been waiting for a very long time, try checking its status using
job-history <jobid>. If you see Allocated RAM/CPU above 5gb on Puma or above 6gb on Ocelote, then you are queued for the high memory node which can have very long wait times. To queue for a standard node, cancel your job and check that your script has the correct ratios.
If your job is in queue, sometimes SLURM will give you information on why it's not running. This may be for a number of reasons, for example there may be an upcoming maintenance cycle, your group's allocation may be exhausted, you may have requested resources that surpass system limits, or the node type you've requested may be very busy running jobs. We have a list of reason codes in our Running Jobs With SLURM page that will give more comprehensive information on what these messages mean. If you don't see the reason code listed, contact our consultants.
va. To see more information on your allotted hours and the different job queues, see: Allocation and Limits.
Specific Errors
This is most commonly seen with users who have Anaconda or Miniconda initialized in their accounts. For a permanent solution, you can run the following command from an interactive terminal session:
conda config --set auto_activate_base false
This will prevent conda from auto-activating when you first log in and allow you to have more control over your environment. When you'd like to activate anaconda, run conda activate. See this example for information running anaconda workflows in batch with auto-activation disabled.
Scripts created in a Windows environment and transferred to HPC retain hidden carriage returns (^M). You can convert your Windows file to Unix format with:
$ dos2unix <filename>
This happens most frequently for new users. It takes a while to propagate new accounts to all the right places. Come back after a coffee break. However, this can occur in other circumstances. Open a support ticket with hpc-consult.
Add this variable definition before executing the application:
export CUDA_FORCE_PTX_JIT=1
Software and Modules
Yes, when you start an interactive terminal session or submit a batch script, the modules ohpc, gnu8, openmpi3, and cmake are automatically loaded. If your code uses Intel compilers, you will want to manually unload gnu8 and openmpi3 to prevent conflicts.
The exception: If you are working in a terminal in an Open OnDemand interactive desktop session, nothing is loaded by default and you will need to manually load any necessary modules.
R installations can sometimes be frustrating. We have instructions for how to set up a usable R environment, how to diagnose and troubleshoot problems, and steps to help with known troublesome packages documented in in our Using and Customizing R Packages section.
You may also want to take a look under our Popular Packages section in the page mentioned above. This includes instructions for packages that are known to cause issues for users.
Load the module, find the path to the executable by checking the $PATH variable, then list the contents. For example:
module load lammps echo $PATH ls /opt/ohpc/pub/apps/lammps/3Mar20/bin lmp_mpi
There are a few different possibilities:
- You are not in an interactive session. Modules are not available on the login nodes. You may request an interactive session by using the command interactive.
- Your shell is not set to bash. If this is the case, contact our consultants so that they can reset it for you.
You have modified or deleted your ~/.bashrc. If this is the case, open (if the file exists) or create and open (if the file is missing) the file .bashrc in your home directory and add the lines:
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi
If you are able to compile your software you can take advantage of most of the AMD Zen architecture.
| Compiler | Arch-Specific | Arch-Favorable |
|---|---|---|
| GCC 9 | -march=znver2 | -mtune=znver2 |
| LLVM 9 | -march=znver2 | -mtune=znver2 |
Neither of these compiler versions (GCC 9 or LLVM 9) is available on Puma so you will have to build that first. If you use GCC 8.3 you can set znver1 instead.
Unfortunately, Windows applications can't be run on HPC. However, AWS has been used successfully for Windows software with GPU needs. It’s easy to set up, cost effective, and very scalable. Amazon also has a cloud credit for research program available
https://aws.amazon.com/government-education/research-and-technical-computing/cloud-credit-for-research/ [aws.amazon.com]
You may also consider trying Jetstream2, a national resource where you can create and use Windows virtual machines. More information can be found here: https://jetstream-cloud.org/
Intel compilers are optimized for Intel processors. There is some debate around the concept of unfair CPU dispatching in Intel compilers. By default, software on the HPC clusters is built with GCC (on Puma it is GCC 8.3). This is in keeping with our preference for community software.
You need to belong to a special group called g03. You can request to be added by submitting a help ticket. This is a constraint in Gaussian that other modules do not have.
Ansys has the Distributed capability built in to increase performance. Ansys uses the Intel compiler and so uses Intel MPI. By default, we load OpenMPI, so you will need to do this:
module unload gnu8 openmpi3 module load intel module load ansys
Instructions on accessing custom packages are under Accessing Custom Packages from a Jupyter Session in our documentation on Using Python & Python Packages.
Data Storage and Transfer
After creating your HPC Account, your home directory will not be created until you log in for the first time. Without your home directory, you will not be able to transfer your data to HPC. If you are struggling and receiving errors, sign into your account either using the CLI through the bastion or logging into OnDemand and then try again.
If you are using something like SCP and are receiving errors, make sure your hostname is set to filexfer.hpc.arizona.edu (not hpc.arizona.edu).
Unfortunately, no. Backups are not made and anything deleted is permanently erased. It is impossible for us to recover it. To ensure your data are safe, we recommend:
- Make frequent backups, ideally in three places and two formats. Helpful information on making backups can be found on our page Transferring Data.
- Use rm and rm -r with caution as these commands cannot be undone! Consider using rm -i when removing files/directories. The -i flag will prompt you to manually confirm file removals to make really sure they can be deleted.
- You can open a support ticket to request assistance. Files that are deleted may not have been removed from the storage array immediately (though this is not guaranteed), don't wait more than a few days.
Endpoint too busy: This is most commonly seen when users are transferring directories to Google Drive. This is because Google has user limits restricting the number of files that can be transferred per unit time. When many files are being transferred at once, that limit may be exceeded. Globus will automatically hold the transfer until the limit is reset at which point it will continue. One way to avoid this is to archive your work prior to the transfer (e.g. in .tar.gz form). Additionally, archiving will also speed up your transfers considerably, sometimes by orders of magnitude.
Fatal FTP Response, PATH_EXISTS: Globus is finicky about the destination endpoint. If you get this error, check to see whether duplicate files/directories exist at the destination. This can happen frequently with Google Drive as multiple files/directories can exist in the same location with the same name. If duplicates exist, try moving, removing, or renaming them and reinitiate the transfer.
In our last maintenance update on July 20th, one of the changes was to ensure HIPAA compliance on the Data Transfer Nodes (DTNs). This change included the insertion of required text:
Authorized uses only. All activity may be monitored and reported.
This change breaks SCP activity. Not in all cases but frequently with WinSCP, Filezilla and from a terminal. Terminal activity will likely still work from Linux or MacOS.
The solution is to not use SCP (SCP is considered outdated, inflexible, and not readily fixed) and to use a more modern protocol like SFTP and rsync. Info on using SFTP:
- Putty supports SFTP with the “PSFTP” command
- For FileZilla, in the Toolbar, click on Edit and Settings, then click on SFTP
- For Cyberduck, choose SFTP in the dropdown for protocols.
Choose SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol), and use filexfer.hpc.arizona.edu as the Server. May enter Username and Password, and unselect “Add to KeyChain”.
For Mac, Cyberduck can be used. For version 8.4.2, select Go then Disconnect before clicking on Quit Cyberduck.
The recent Cyberduck patch 8.4.4 has created problems with two-factor authentication which is required to access filexfer.hpc.arizona.edu. Adding a SSH Keys is suggested.
For Windows, WinSCP and FileZilla are recommended.
If your home directory is full and you can't find what is taking up all the space, it's possible the culprit is a hidden file or directory. Hidden objects are used for storing libraries, cached singularity/apptainer objects, saved R session, anaconda environments, configuration files, and more. It's important to be careful with hidden, or "dot", files since they often control your environment and modifying them can lead to unintended consequences.
To view the sizes of all the objects (including hidden) in your home, one quick command is du -hs $(ls -A ~) , for example:
[netid@junonia ~]$ du -hs $(ls -A ~) 32K Archives 192M bin 4.7G Software 46M .anaconda 1.9M .ansys 4.0K .apptainer 16K .bash_history 4.0K .bash_logout 4.0K .bash_profile 12K .bashrc 20M ondemand
Clearing out unwanted objects, moving data to a location with more space (e.g. /groups or /xdisk), and setting different defaults for data storage (e.g., resetting your apptainer cache directory or setting new working directories for Python/R) can help manage your home's space.
Unfortunately, without active university credentials it is not possible to access HPC compute or storage resources. External collaborates who need ongoing access may apply for Designated Campus Colleague, or DCC, status. This is a process done through HR and will give the applicant active university credentials allowing them to receive HPC sponsorship.
Otherwise, data will need to be moved off HPC and made available on a mutually-accessible platform. This may include (but is not limited to): Google Drive, AWS S3, Box, and CyVerse's Data Store.
xdisk
Yes! A PI can add a trusted group member as a delegate by following the instructions in our Research and Class Groups page. Once a group member is added as a delegate, they can manage the group's xdisk allocation on behalf of their PI in the user portal.
A group's PI owns the /xdisk allocation. By default, your PI has exclusive read/write/execute privileges for the root folder /xdisk/PI.
By default, members of a research group only have write access to their subdirectories under /xdisk/PI. If they so choose, a PI may allow their group members to write directly to /xdisk/PI by running one of the following commands:
| Command | Result |
|---|---|
| Group members can see the contents of the directory with ls, but may not access it or make modifications (e.g. add, delete, or edit files/directories) |
| Group members can access the directory and see files but cannot make modifications (e.g. add, delete, or edit files/directories) |
| Group members are granted full read/write/execute privileges. |
When an /xdisk allocation is created, a subdirectory is automatically generated for and owned by each individual group member. If the directory /xdisk/PI does not have group privileges, group members may not access the root directory, but may access their individual spaces by:
$ cd /xdisk/PI/netid
If a user joins the group after the xdisk was created and /xdisk/PI is not writeable for group members, contact our consultants and they can create one.
Typically when an /xdisk allocation is created, it will automatically generate a directory for each group member. In the unlikely event that it doesn't or, more commonly, a group member is added after the allocation has been created, either the PI may manually create a directory or, if the root directory is group writable, the user may create one themselves. If the group's /xdisk does not have full group permissions, the PI may run:
$ mkdir /xdisk/PI/netid
then can reach out to our hpc consultants to request an ownership change.
No, the full /xdisk allocation is available for every member of the group. It's up to group members to communicate with one another on how they want to utilize the space.
If you're getting errors using xdisk commands in a terminal session, check that you are on a login node. If you are on the bastion host (hostname: gatekeeper), are in an interactive session, or are on the filexfer node, you won't be able to check or modify your xdisk. When you are on a login node, your terminal prompt should show the hostname junonia or wentletrap. You can also check your hostname using the command:
$ hostname
If you're trying to extend your group's allocation but are seeing something like:
(puma) [netid@junonia ~]$ xdisk -c expire -d 1 invalid request_days: 1
for every value you enter, your xdisk has likely reached its maximum time limit. To check, have a delegate or PI go to portal.hpc.arizona.edu, click Manage XDISK, and look at the box next to Duration. If you see 300, your allocation cannot be extended further.
If your allocation is at its limit, you will need to back up your data to external storage (e.g., a local machine, lab server, or cloud service). Once your xdisk has been removed (either by expiring or through manual deletion), you can immediately create a new allocation and restore your data. Detailed xdisk information can be found on our HPC High Performance Storage page. You may also want to look at our page on Transferring Data.
No, once an xdisk has reached its time limit it will expire. It's a good idea to start preparing for this early by making frequent backups and paying attention to xdisk expiration emails.
Once an xdisk expires, all the associated data are deleted. Deleted data are non-retrievable since HPC is not backed up. It's advised to keep frequent backups of your data on different platforms, for example a local hard drive or a cloud-based service, or (even better) both! Check our Storage documentation for more information on alternative storage offerings.
Onsite Rental Storage
AWS Tier 2 Storage
Official AWS FAQs are here:https://aws.amazon.com/s3/faqs/
You should check the Amazon site: https://aws.amazon.com/s3/pricing/?nc=sn&loc=4
As of March 2022:
- Frequent Access Tier, First 50 TB / Month $0.023 per GB
- Frequent Access Tier, Next 450 TB / Month $0.022 per GB
- Frequent Access Tier, Over 500 TB / Month $0.021 per GB
Research Desktop Attached Storage (RDAS)
This error is seen if you are not connected to the University VPN.
R-DAS is not mounted on the HPC compute nodes or login nodes, and is not meant for running computations. But you can follow the steps below to share data between your R-DAS allocation and your HPC storage (/home, /groups, /xdisk):
- Follow the steps in Virtual Desktop to launch an Interactive Desktop session. This will start a Linux environment with the Mate desktop environment in your browser.
- Open the file manager (also known as Caja) in the Interactive Desktop. You can open it by either clicking the file drawer icon in the top bar, or by selecting Applications > System Tools > Caja.
Follow the steps under Accessing Your R-DAS Allocation - Linux (GUI) to connect to your R-DAS allocation from the Interactive Desktop.
Please do not run the
sudocommands mentioned in Accessing Your R-DAS Allocation - Linux (GUI) on the HPC. All the necessary software are already installed on HPC, you do not have to install anything more.
You can now transfer data between your R-DAS allocation and your HPC storage.
Secure Services
You will first need to request access. Follow the instructions in our Secure HPC page to see all the steps that are required.
It's possible you're not connected to the VPN. You will need to be connected to access any Soteria resources.
The easiest way to transfer your data to Soteria is using Globus. We have a high assurance endpoint set up accessible under the endpoint UA HPC HIPAA Filesystems
It depends.
You do not need your personal computer's Globus endpoint set to high assurance for the purposes of transferring data to Soteria using our UA HPC HIPAA Filesystems endpoint. HIPAA requires data transfer auditing. We log transfers on our DTN that use the HIPAA endpoint, regardless of the client's managed status.
If you are working with another institution/endpoint that only allows connections from high assurance endpoints, then you must enable High Assurance during your Globus Personal Connect configuration process. This requires that you are added to our Globus subscription which can be done by opening a support ticket to request help from our consultants. Your endpoint must be set to public to allow us to add you. Once you have been added, you may set your endpoint to private.